The concept of forced air technology has revolutionized the way we approach various industrial and commercial applications, from heating and cooling systems to material processing and more. At its core, forced air technology relies on the principle of using air movement to achieve specific goals, such as temperature control, material transport, or even ventilation. In this article, we will delve into the world of forced air technology, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and applications in various industries.
Forced Air Systems: How They Work
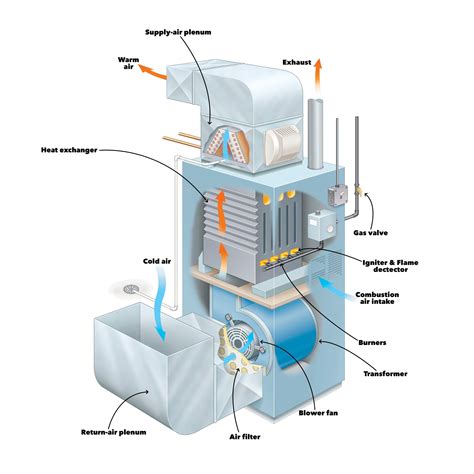
Forced air systems operate by using fans or blowers to circulate air through a network of ducts or channels. This airflow is then used to achieve a specific purpose, such as heating or cooling a space, or transporting materials. The system typically consists of several components, including:
- A fan or blower: This is the heart of the forced air system, responsible for creating the airflow.
- Ducts or channels: These are the pathways through which the air flows.
- Diffusers or outlets: These are the points at which the air is released into the environment.
- Controls: These are the systems that regulate the airflow, temperature, and other parameters.
Benefits of Forced Air Technology
Forced air technology offers several benefits across various industries. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Energy efficiency: Forced air systems can be highly energy-efficient, especially when compared to traditional heating and cooling methods.
- Cost-effectiveness: By using forced air technology, businesses can reduce their energy costs and save money in the long run.
- Flexibility: Forced air systems can be designed to meet specific needs and applications, making them highly versatile.
- Improved air quality: Forced air systems can be designed to improve indoor air quality by removing pollutants and allergens.
Applications of Forced Air Technology
Forced air technology has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common uses include:
- Heating and cooling systems: Forced air systems are commonly used in HVAC systems to heat and cool buildings.
- Material processing: Forced air technology is used in various material processing applications, such as drying, curing, and conveying.
- Ventilation systems: Forced air systems are used in ventilation systems to remove pollutants and improve indoor air quality.
- Agricultural applications: Forced air technology is used in agricultural applications, such as grain drying and livestock ventilation.

Types of Forced Air Systems
There are several types of forced air systems, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Centrifugal systems: These systems use a centrifugal fan to create airflow.
- Axial systems: These systems use an axial fan to create airflow.
- Mixed-flow systems: These systems use a combination of centrifugal and axial fans to create airflow.
Design Considerations for Forced Air Systems
When designing a forced air system, there are several factors to consider. Some of the most important design considerations include:
- Airflow rate: The airflow rate must be sufficient to meet the specific needs of the application.
- Pressure drop: The pressure drop across the system must be minimized to ensure efficient operation.
- Noise level: The noise level of the system must be considered, especially in applications where noise is a concern.
- Cost: The cost of the system must be considered, including the initial investment and ongoing operating costs.

Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Forced Air Systems
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the efficient operation of forced air systems. Some common maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning the fans and ducts: Regular cleaning is necessary to remove dirt and debris that can accumulate and reduce airflow.
- Checking the controls: The controls must be checked regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Lubricating the fans: The fans must be lubricated regularly to ensure smooth operation.
Common issues that can arise with forced air systems include:
- Reduced airflow: This can be caused by a variety of factors, including clogged ducts or faulty fans.
- Increased energy consumption: This can be caused by a variety of factors, including inefficient operation or faulty controls.
- Noise: This can be caused by a variety of factors, including faulty fans or loose connections.
Conclusion
Forced air technology has revolutionized the way we approach various industrial and commercial applications. By understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and applications of forced air technology, businesses can harness its power to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or just starting out, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of forced air technology and its many uses.
Gallery of Forced Air Technology






What is forced air technology?
+Forced air technology is a method of using air movement to achieve specific goals, such as temperature control, material transport, or ventilation.
What are the benefits of forced air technology?
+The benefits of forced air technology include energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and improved air quality.
What are the common applications of forced air technology?
+Forced air technology has a wide range of applications, including heating and cooling systems, material processing, ventilation systems, and agricultural applications.